At West High School, each teacher is maintaining a Blackboard course for each face-to-face course taught. Within the course the instructors provide students (and their parent(s)/guardian(s)) access to a course-focused Google Calendar, access to resources and assignments for the course, and possibly even some multimedia content related to the course. While the implementation is in its earliest stages at West, students are already adapting and responding to the availability of the resources digitally.
Land recently asked 40 of her Grade 9 students enrolled in the West House (a pilot of a traditional "house" structure where teachers co-plan, co-teach, and converse about student progress with a cross-curricular emphasis) how they are using and feeling about the Blackboard course she maintains. There responses add some clarity to the question of how a resource like Blackboard can impact the learning experience for students.
Reviewing the Responses
Points to consider:
- 40 % said they like the calendar, indicating that these students appreciate clarity about what is planned for and expected of them
- 38% of the student indicated that they like that they like how the site is organized (25%) or say that it helps them with homework (13% -- orange)
- Only 5% of the students said "Nothing", although it was an available survey option
Points to consider:
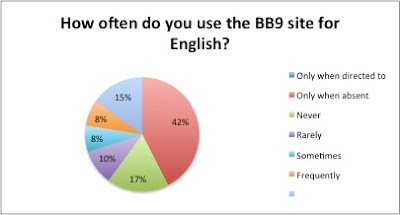
- 61% of students said that they use the course calendar "Sometimes" (23%) or "Frequently" (38%) -- an indicator that students are engaging with the course calendar even though it is not required
- 10% of students report using the calendar if absent, a sign that students take responsibility for missed coursework if required to
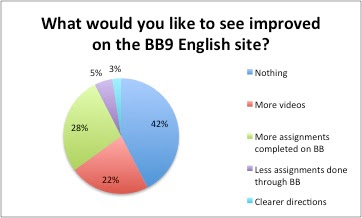
Question: What would you like to see improve (or more of) on the Blackboard 9 English course?
- 22% of students asked for more videos to be available -- a possible sign that some students prefer instruction delivered in a "flipped," on-demand model
- Only 3% of students asked for "Clearer Directions" on the course, suggesting that students have sense of what they are asked to do when engaging with Blackboard content
- 42% of the students surveyed were seemingly content with the organization of Blackboard, as they suggested nothing needed to be improved at this time
Points to consider:
- The results suggest that students are not presently accessing Blackboard consistently as a critical source for interacting with instructional content
- The data may speak to the lack of consistently accessible technology for students to access a Blackboard course in as needed in the classroom